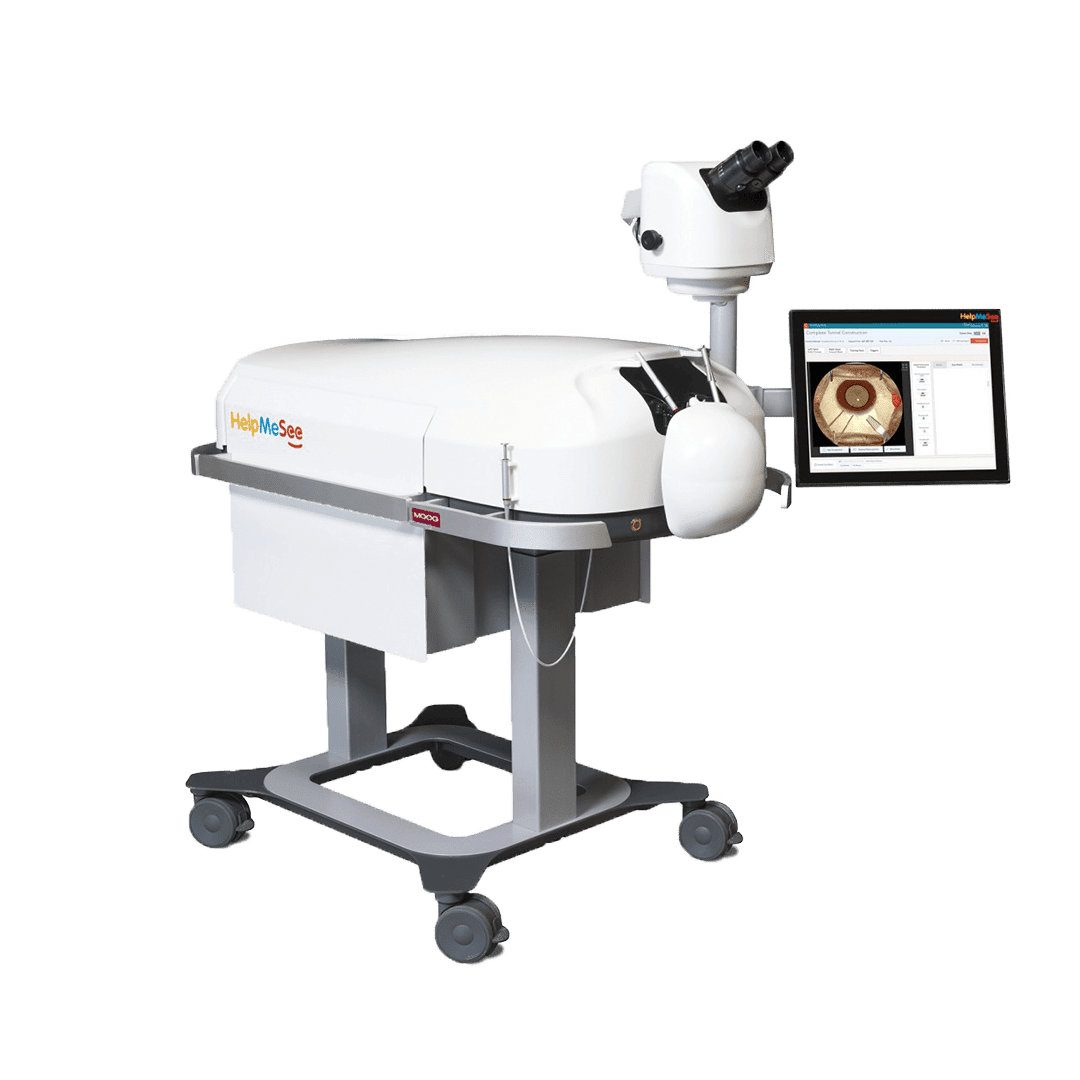
Revolutionizing Eye Surgery Training:
HMS simulator study featured in Nature
A new study unveiled in Nature, one of the world’s most prestigious scientific journals, assessed for the first time the extrinsic and intrinsic construct validity of the Phacoemulsification modules of HelpMeSee (HMS) Surgery simulator, proving it is a highly promising cataract training module.
HelpMeSee (HMS) is a non-profit organization whose mission is to end cataract blindness by vastly increasing access to treatment through the training of Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery.
CONTEXT
Cataract, which is defined as lens opacification, is the primary cause of reversible blindness in the world, affecting 94 million people worldwide. The cataract treatment is surgical with Phacoemulsification (Phaco) remaining the standard procedure for over three decades in developed countries.
The Ophthalmology Department of Strasbourg University Hospital and Gepromed Education Department, also in Strasbourg, conducted a study to assess validity evidence of the new Phacoemulsification module of the HelpMeSee (HMS) virtual reality simulator.
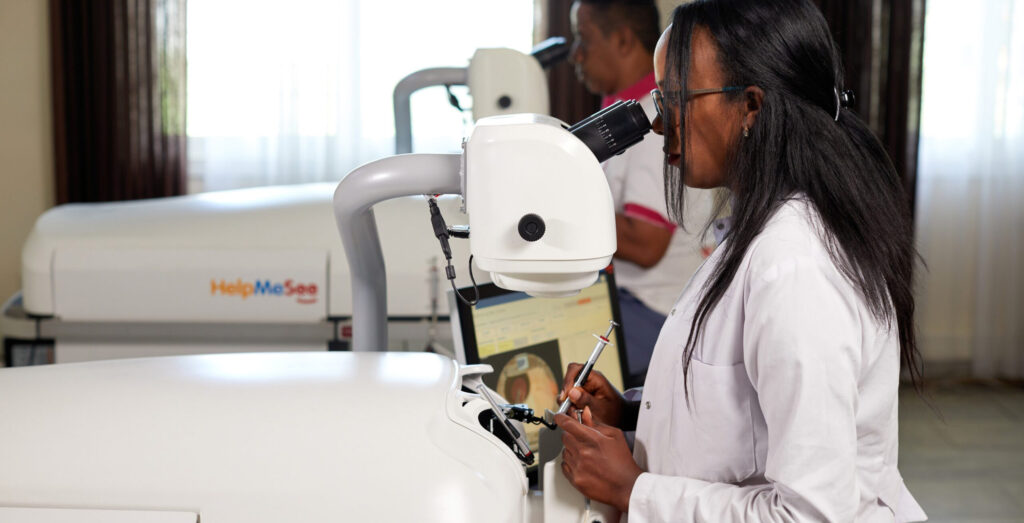

© HelpMeSee
BACKGROUND
Cross-sectional study: 20 surgeons divided into 2 groups based on their experience over or under 300 cataract surgeries
Predominantly right-handed males, with expert surgeons averaging 44 years and intermediate surgeons 29 years of age
Expert surgeons had completed around 2000 phacoemulsification surgeries compared to 150 by intermediates
Surgeons filled out a background survey covering their phacoemulsification experience and prior simulator use
Single-session simulations on 2 simulators, including HMS simulator
MEASURES AND METHODS
Grip fatigue evaluation: handgrip strength was measured pre- and post-simulation
Realism of the simulation: surgeons rated the perceived realism on a seven-point Likert scale
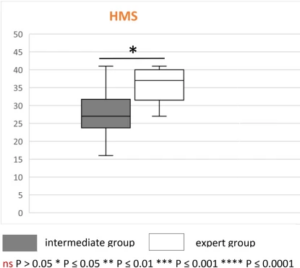
Construct validity of HMS simulator evaluation based on the difference in total and module scores between both groups. Intrinsic validity evaluated to distinguish between expert-level surgeons (> 300 surgeries) and intermediate-level surgeons (< 300 surgeries). Extrinsic validity focused on correlating the overall HMS score with the score previously validated for another simulator
🔎 RESULTS
Extrinsic and intrinsic construct validity of the Phacoemulsification module
Ability to differentiate the level of the surgeons (beginner, intermediates, experts)
Tactile feedback (incision, hydrosuture) allowing surgeons to practice incisions and experience the sensations of instrument entry and exit, as well as hydrosuturing
Less grip fatigue post-simulation for experts compared to intermediates
Potential to broaden simulation-based training by targeting diverse populations
INSIMO & HELPMESEE:
PARTNERS TO ERADICATE CATARACT BLINDNESS
Training on a virtual reality simulator improves several aspects of surgical training, reducing complications and total operating time. It also has the benefit of improving user confidence and reducing stress levels.
HMS simulator is the most advanced interactive eye physics simulation ever developed:
MSICS & PHACO procedures incl. complications
Precise microsurgery control, rendering & feeling
Micro gestures haptic feedback
Detailed evaluation of procedures